Archive
Living in the Age of Edited Realities
Emerging technologies have been gradually reshaping our perception of reality. This may have begun with electronic games (or perhaps early Reality TV), multiplayer online role playing games (MORPG), then came social media, fake news, and various Extended Reality (XR) technologies, including the Metaverse. The addition of AI generated deep fakes and now multi-modal Generative AI has dramatically raised the stakes and begs the question, are we now living in an age of edited realities?
Read more…Generative AI / Generative IP (Part 3: Now What?)
My previous posts described the rise of Generative AI applications and their usability super-powers, as well as their implications for mass AI adoption, ethics and intellectual property, but the question remains – How should the average person respond to what some describe as a critical and transformative step in our collective human experience and cultural evolution?
Read more…Generative AI / Generative IP (Part 2: So What?)
In my first post on this topic, I described how the most striking aspect of the sudden rise in popularity of generative AI models may be the accessibility and ease of use of such applications as ChatGPT, which seem to be approaching a tipping point towards mass adoption. Could this be a much anticipated AI Summer, as opposed to AI Winters of the past? What are the key implications of these developments?
Read more…Generative AI / Generative IP (Part 1: What?)
What makes such Generative AI applications as: ChatGPT, Dall-E, Codex, or MidJourney and Stable Diffusion so compelling? Is it the seemingly miraculous leap in capability, application and user experience? Or is it something to do with the timing, (at the tail-end of a great pandemic), and/or the tantalising promise of even greater things to come? And what has all this got to do with Intellectual Property anyway? Well, why don’t you jump on my multi-carriage train of thought to find out…
Read more…ChatGPT and Intellectual Property
ChatGPT has taken the world by storm, and it is only at GPT version 3.5! As ever, given its proximity and ability to generate creative content (e.g. text, art, music, poetry, videos and games), the first question that comes to mind, as indeed it has with many others, is what are the implications for Intellectual Property, especially copyright? Is it finally time to update and upgrade that most artificial of property rights to something befitting the 21st century?
In true spirit of enquiry, I had to do the needful and ask ChatGPT for its views on the future of Generative AI and Intellectual Property, and below is a screenshot + transcript of the most-impressive sub-minute responses I got to both my questions:
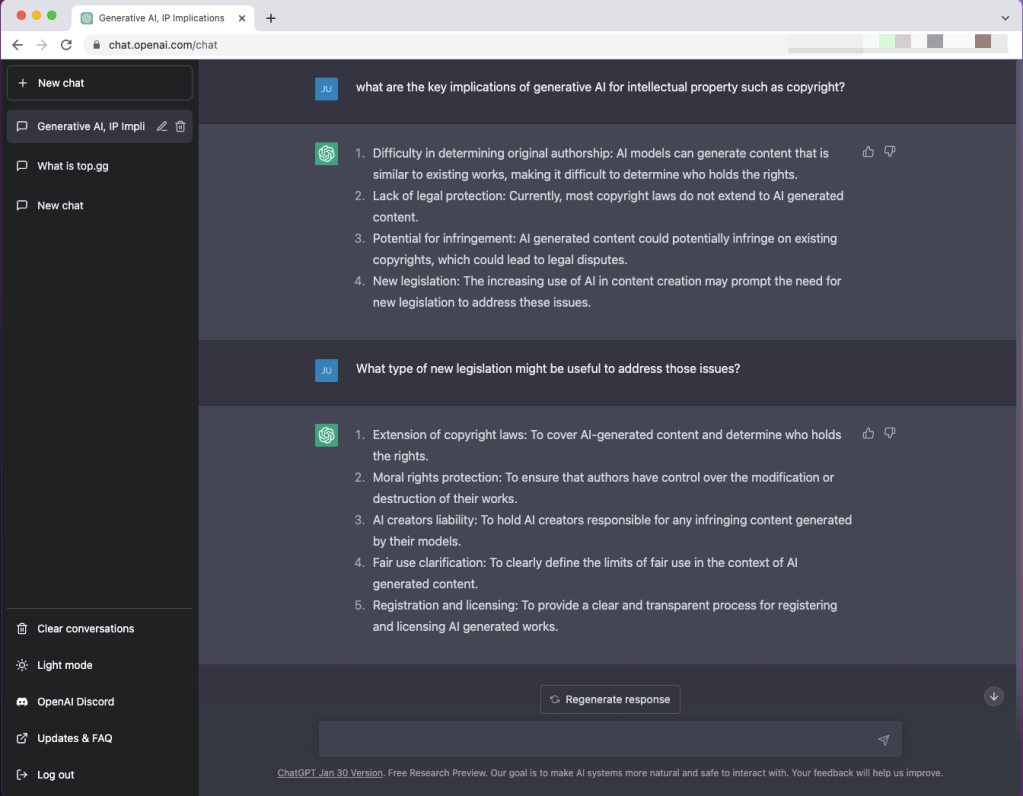
Transcript:
Q1: what are the key implications of generative AI for intellectual property such as copyright?
ChatGPT:
- Difficulty in determining original authorship: AI models can generate content that is similar to existing works, making it difficult to determine who holds the rights.
- Lack of legal protection: Currently, most copyright laws do not extend to AI generated content.
- Potential for infringement: AI generated content could potentially infringe on existing copyrights, which could lead to legal disputes.
- New legislation: The increasing use of AI in content creation may prompt the need for new legislation to address these issues.
Q2: What type of new legislation would be useful to address those issues?(i.e. of AI content and intellectual property)
CHATGPT:
- Extension of copyright laws: To cover AI-generated content and determine who holds the rights.
- Moral rights protection: To ensure that authors have control over the modification or destruction of their works.
- AI creators liability: To hold AI creators responsible for any infringing content generated by their models.
- Fair use clarification: To clearly define the limits of fair use in the context of AI generated content.
- Registration and licensing: To provide a clear and transparent process for registering and licensing AI generated works.
What can I say – ChatGPT must have read my mind!
I can certainly understand why authors, bloggers and some journalists might be tempted to use this service to augment or create their content, but I have chosen not to do so on this occasion. A man has his fast waning pride to hold on to. What’s more, I feel a series of hand-crafted posts on this topic coming soon, so watch this space!
UPDATE:
Below are the links to my 3-part blogpost series entitled “Generative AI / Generative IP”. They represent my train of thoughts which I’ve chunked into the following parts that describe the: What.., So What.., and Now What.., as follows:
- What? – The first carriage on my metaphorical train looks at current state AI and the amazing capabilities provided with transformers and other generative models.
- So What? – This is swiftly followed in the second carriage by an exploration of certain key implications, particularly with regards to jobs, IP & Ethics.
- Now What? – The final carriage concludes with some admonitions, premonitions and recommendations for the way forward. So, all aboard!
WIPF2022: A different mindset for emerging technologies and intellectual property.
As promised, this is a summary post with my top 5 takeaways from the recent World IP Forum 2022 conference I attended in Bangkok, Thailand.
What a pleasure it was to meet, mingle and exchange ideas with a global cast of IP professionals across three days of wall-to-wall conversations, panels and presentations by experts in the legal profession, international business and government agencies. Kudos to the organisers, especially Navi Agarwal and Jeet Agarwal for a fantastic show with a truly international worldview.
Top five learnings and takeaways from WIPF2022 Bangkok:
- Patents are huge – the level of interest and discourse around patents reflect, in my opinion, their powerful potential to play a major role in redefining the IP landscape for a fast emerging world of tomorrow.
- DABUS (AI owned patents) – this is really doing the rounds as a bell weather case that shows up constraints and limitations of current legal frameworks, expert understanding and jurisdictional perspectives on emerging technologies and IP.
- AI and Personhood – exhaustive discussions on why AI can’t be recognised as author / owner of IP. This is mainly down to AI not being considered a natural person – a key requirement for IP ownership in many places. I wonder if and when that is likely to change with more DABUS-like cases sure to come along.
- Rise of the techno-lawyers – By the way, it seems I’m encountering more and more legal professionals with a technical background – this is a most interesting trend, and has left me thinking perhaps I ought to study IP law too – hmmm!
- Still early days – And still lots of room to explore, understand and adapt emerging technologies and impact. Call to Action: read up and research AI, Blockchain and other emerging technologies because in 5 years or less they’ll impact your practice.
My conclusion – It’ll require a different mindset to harness opportunities and/or tackle challenges presented by emerging technologies and intellectual property. For example, one of the most insightful questions I heard on the Metaverse panel was: …why use web2 rules for web3 worlds – i.e. how and why are we trying to figure out the rules of metaverse using only real world legal systems and lawyers? …Duh!
My panel presentation on emerging technologies and the future of content & IP is centred on this last point, as I introduced a three-point framework for looking at future state systems and how they might apply to IP considerations. More to come on this topic so watch this space!
Intellectual Property and Emerging Technologies
A new course certificate – Yes, another one. There’s a theme here…

I must say this one was particularly challenging, but even more rewarding, as it helped reshape and validate my notion that no single one of these ’game changer’ technologies can match over-hyped expectations all by themselves. Instead, and perhaps obviously, it’ll take certain combinations and mashups of two or more of these technologies to create the right value propositions for robust, real-world applications that can finally meet and / or exceed current expectations.
As a result, I remain steadfast in my conviction, and even doubling down my commitment to stay at the sharp end of emerging technology and the impact on society, businesses and individuals.
For example, I’m excited to be on a panel discussing Emerging Technology and Intellectual Property at the World IP Forum 2022 event taking place on 10th-12th October, in Bangkok Thailand. I will be talking about the role of emerging technologies and the next phase of digital content and rights management. Intellectual Property, such as Copyright, must evolve to keep pace with new technologies and novel uses of the works they’re designed to protect, (in both physical and digital realms, as well as in the spaces between them).
From past experience, events such as these offer great opportunities to share and learn from others, as well as networking with speakers, moderators and attendees. It’s great to be back on the circuit, and and I may do a summary post following the event, or perhaps even a podcast as Gen Z folks supposedly demand.
Are NFTs the future of digital IP and the creative world, or just a remix of DRM and all its woes? (Part 5)
This is last in a series of posts to share some observations, opinions and conclusions on this intriguing technology which sits squarely at the intersection of digital, creativity and intellectual property. The topic is broken down into the following parts:
- What are NFTs (and the non-fungibility superpower)?
- What has this got to do with Intellectual Property (and content protection)?
- Does it mean that NFTs are like DRM remixed?
- How does it affect the creative industry today and in the future?
- Summary observations and conclusions.
Are NFTs the future of digital IP and the creative world, or just a remix of DRM and all its woes? (Part 4)
This is fourth in a series of posts to share some observations, opinions and conclusions from playing with this intriguing technology that sits squarely at the intersection of: digital technology, creative content and intellectual property. The topic is broken down into the following parts:
- What are NFTs (and the non-fungibility superpower)?
- What has this got to do with Intellectual Property (and content protection)?
- Does it mean that NFTs are like DRM remixed?
- How does it affect the creative industry today and in the future?
- Summary observations and conclusions.
Are NFTs the future of digital IP and the creative world, or just a remix of DRM and all its woes? (Part 3)
This is third in a series of posts to share some observations, opinions and conclusions from playing with this intriguing technology that sits squarely at the intersection of digital technology, creative content and intellectual property. The topic is broken down into the following parts:
- What are NFTs (and the non-fungibility superpower)?
- What has this got to do with Intellectual Property (and content protection)?
- Does it mean that NFTs are like DRM remixed?
- How does it affect the creative industry today and in the future?
- Summary observations and conclusions.
